|
Related Topics: |
|
|
|
Current News |
|
Chemistry A to Z |
|
About Internetchemistry |
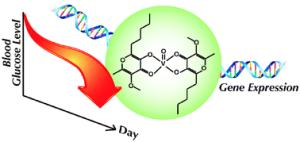
Garlic chemical tablet treats diabetes I and II |
|
When Hiromu Sakurai and colleagues from the Suzuka University of Medical Science, Japan, gave the drug orally to type I diabetic mice, they found it reduced blood glucose levels. |
|
The drug is based on vanadium and allaxin, a compound found in garlic, and its action described in an Advance Article from Metallomics available free online. The first issue of the new journal will be published in 2009. In previous work they had discovered the vanadium-allaxin compound treated both diabetes types when injected, but this new study shows the drug has promise as an oral treatment for the disease. Type I diabetes (insulin dependent) is currently treated with daily injections of insulin, while type II (non-insulin dependent) is treated with drugs bearing undesirable side-effects - the authors note neither treatment is ideal. The researchers aim to test the drug in humans in future work. |
|
|
|